Design and Analysis of Algorithm Lab 11 | Read Now
Design and Analysis of Algorithm Lab 11
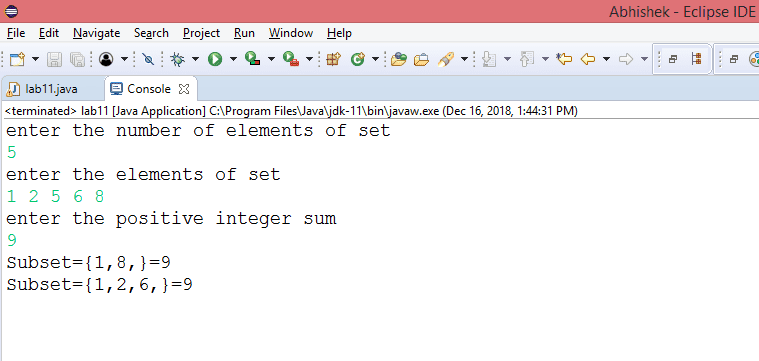
11] Design and implement in java to find a subset of a given set S={S1, S2,….,Sn} of n positive integers whose SUM is equal to a given positive integer d. For example, if S={1,2,5,6,8} and d=9, there are two solutions {1,2,6} and {1,8}. Display a suitable message, if the given problem instance doesn’t have a solution.
11] Program code
import java.util.Scanner;
import static java.lang.Math.pow;
public class lab11
{
void subset(int num,int n, int x[])
{
int i;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
x[i]=0;
for(i=n;num!=0;i--)
{
x[i]=num%2;
num=num/2;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int a[]=new int[10];
int x[]=new int[10];
int n,d,sum,present=0;
int j;
System.out.println("enter the number of elements of set");
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
n=sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("enter the elements of set");
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
a[i]=sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("enter the positive integer sum");
d=sc.nextInt();
if(d>0)
{
for(int i=1;i<=Math.pow(2,n)-1;i++)
{
lab11 s=new lab11();
s.subset(i,n,x);
sum=0;
for(j=1;j<=n;j++)
if(x[j]==1)
sum=sum+a[j];
if(d==sum)
{
System.out.print("Subset={");
present=1;
for(j=1;j<=n;j++)
if(x[j]==1)
System.out.print(a[j]+",");
System.out.print("}="+d);
System.out.println();
}
}
}
if(present==0)
System.out.println("Solution does not exists");
}
}
Output